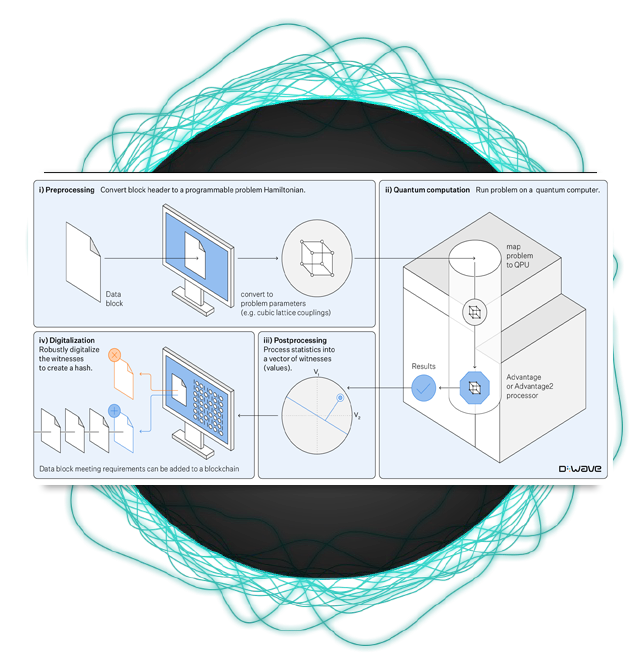
Quantum Blockchain Architecture
In a new research paper, “Blockchain with Proof of Quantum Work,” D-Wave introduces a novel blockchain architecture that could enhance blockchain security and efficiency by using techniques from its quantum supremacy demonstration.

Join us at Qubits March 31 and April 1
Join D-Wave for an inspiring 2-day conference in Scottsdale, Arizona, where you can connect with quantum computing trailblazers, thought leaders, and adopters from around the world. Attend in person or watch the live stream. Register today.
Distributed Quantum Computing for Blockchain
D-Wave executes the first-ever demonstration of distributed quantum computing, deploying blockchain across four cloud-based annealing quantum computers in Canada and the United States. The new research paper, “Blockchain with Proof of Quantum Work,” highlights how D-Wave built and tested a “proof of quantum” algorithm that uses quantum computation to generate and validate blockchain hashes. The resulting techniques demonstrated that D-Wave’s quantum blockchain architecture could enhance security and significantly reduce electricity costs.
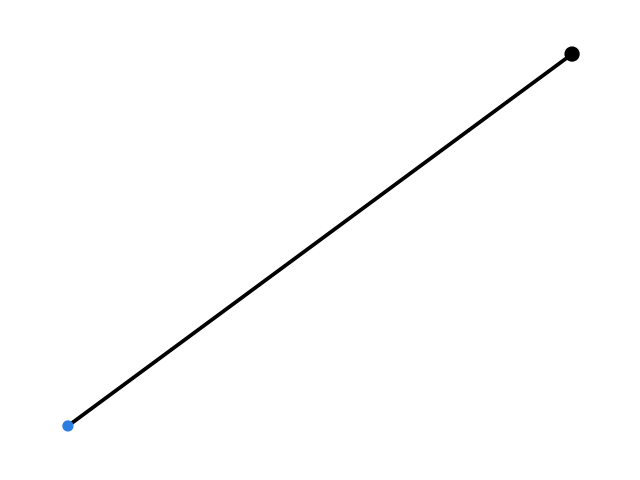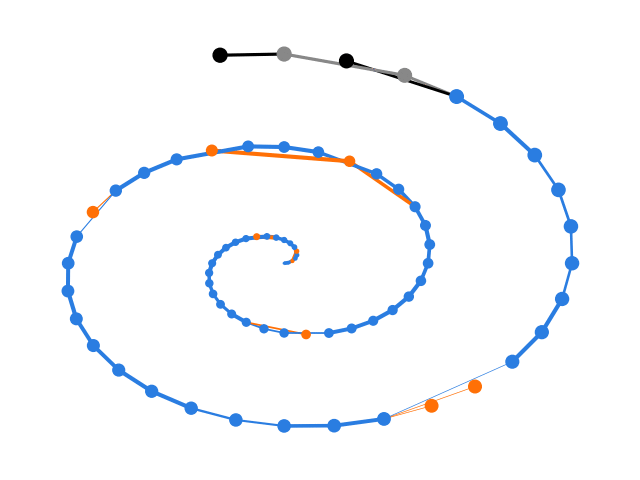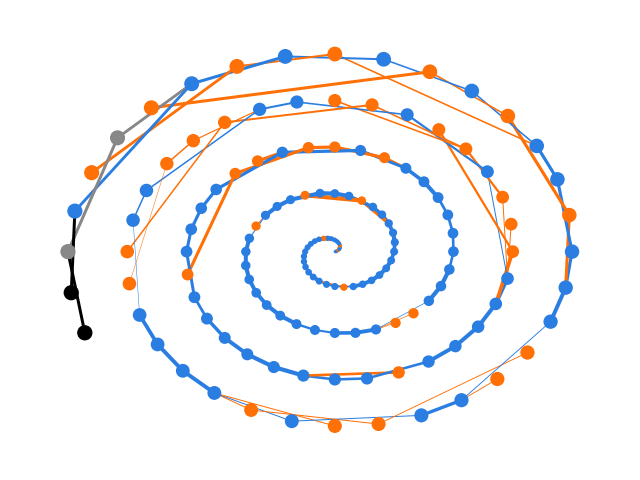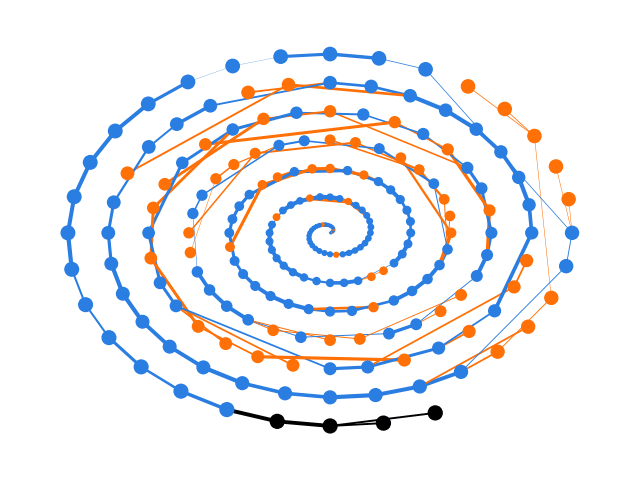
D-Wave's research is the first time a blockchain has successfully operated on a distributed network of four quantum computers.
First to Demonstrate Quantum Supremacy on Useful, Real-World Problem
Blockchains rely on hashing, a mathematical function that acts like a digital fingerprint. Hashing is used to encrypt transactions, and "proof of work" algorithms validate those transactions. Classical computers currently used for hashing and proof of work consume significant amounts of electricity. Each year, the power consumption of Bitcoin alone—just one application of blockchain— is estimated to be comparable to the power consumption of the entire country of Poland.
The research introduces a new quantum-powered method to securely and efficiently create hashes by mapping mathematical functions to the complex programmable spin glasses simulated in D-Wave's recent supremacy demonstration. The proof of quantum algorithm presented in the paper is designed to incorporate hashes generated by a quantum computer, excluding classical computation from the process and adding an enhanced layer of security.
An illustration from a new research paper published by D-Wave introducing a novel blockchain architecture that leverages the company’s quantum supremacy achievement. The illustration depicts how a “proof of quantum” algorithm developed by D-Wave uses quantum computation to generate and validate blockchain hashes.
The Compute
D-Wave scientists deployed the blockchain architecture across four of its cloud-based annealing quantum computers in Canada and the U.S., performing distributed quantum computing for the first time.
The Result
D-Wave’s quantum systems were able to cross-validate each other and facilitate stable blockchain operation for thousands of transaction blocks.
The Impact
D-Wave’s research indicates that using quantum computation for hashing and proof of work could enhance security and require a fraction of the electricity used by classical resources.
Behind the Research
Get Access
The D-Wave annealing quantum computers used in this blockchain application and the supremacy demonstration are available for customers to use today via D-Wave's Leap real-time quantum cloud service.

Qubits Annual User Conference
Qubits 2025, D-Wave's annual user conference, is one of the premier quantum computing events of the year, connecting quantum computing trailblazers, thought leaders and adopters from around the world.

Quantum Realized
D-Wave has developed a clear framework that deflates the hype, helping you develop an informed position on quantum. The framework consists of three simple benchmarks to consider when assessing a particular quantum company’s value.

Leap Quantum Launchpad™ Program
Accelerate your exploration and development of quantum and hybrid-quantum applications with the Leap Quantum LaunchPad™ program.